
Anti-infectieux1,2
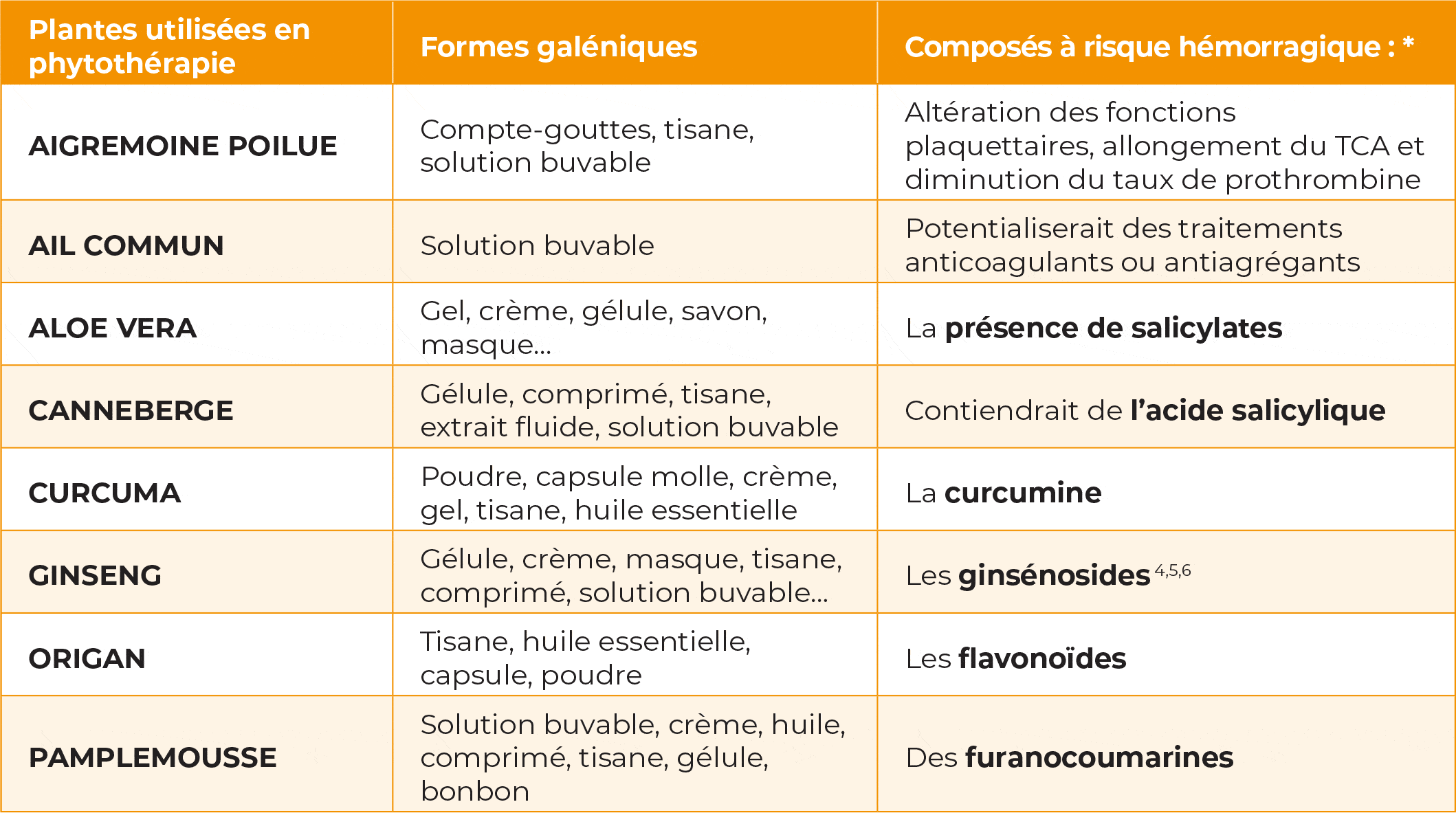
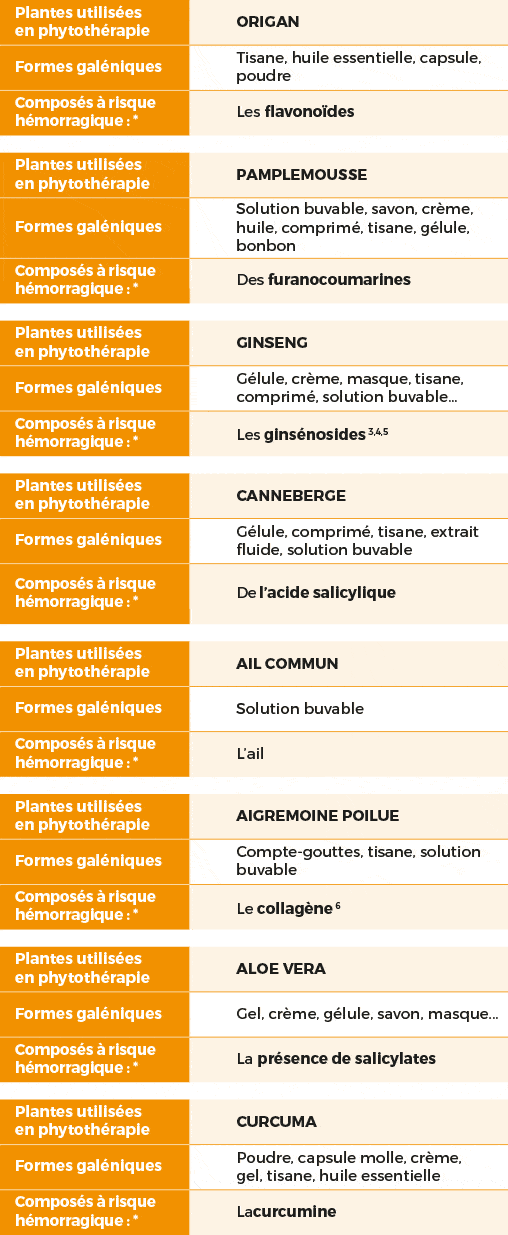

* effet anti-plaquettaire / anticoagulant (donc : allongement du TCA)
→ direct via la voie exogène ou intrinsèque :
par la diminution ou inhibition d’éléments activateurs des plaquettes:
– de la synthèse du taux de prothrombine, donc du relargage de l’ADP par la thrombine et de sérotonine au niveau plaquettaire;
– des groupes sulfhydryles plaquettaires ;
– du métabolisme de l’acide arachidonique, donc de thromboxane A2
– antagoniste du PAF
– augmentant l’adénosine monophosphate cyclique (AMPc) intracellulaire
– Tous capables
→ ou indirect en inhibant les cytochromes CYP3A4 et CYP2C9, entraînant un surdosage en antivitamines K (AVK) chez les patients traités par warfarine
1.
Wong WW, Gabriel A, Patrick Maxwell G, et al. Bleeding risks of herbal, homeopathic, and dietary supplements: a hidden nightmare for plastic surgeons. Aesthetic Surgery J 2012;32:332-46.
2.
Abede W. Review of herbal medications with the potential to cause bleeding: dental implications, and risk prediction and prevention avenues. EPMA J 2019;10:51-64.
3.
Park HJ, Lee JH, Song YB, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of lipophilic fraction from Panax ginseng on cGMP and cAMP in rat platelets and on blood coagulation. Biol Pharm Bull 1996;19:1434- 1439.
4.
Lau AJ, Toh DF, Chua TK, et al. Antiplatelet and anticoagulant effects of Panax notoginseng: comparison of raw and steamed Panax notoginseng with Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolium. J Ethnopharmacol 2009;125:380-386.
5.
Hsu MF, Young JH, Wang JP, et al. Effect of hsien-ho-t’sao (Agrimonia pilosa) on experimental thrombosis in mice. Am J Chin Med 1987;15:43-51.
6.
Teng CM, Kuo SC, Ko FN, et al. Antiplatelet actions of panaxynol and ginsenosides isolated from ginseng. Biochim Biophys Acta 1989;990:315-320.
